College Algebra
TEXT: College Algebra, 3rd Edition, by Mark Dugopolski
NOTE: Effective in the Fall 2004 Semester, students taking College Algebra
will not be
allowed to use a calculator on tests.
My Math Lab: All students enrolled in MA 1313 College Algebra will be
required to set up an account using the
software My Math Lab. This will be done during the first week of classes. The
software will come packaged with
every new textbook and may be purchased either from the bookstore or directly
from Addison-Wesley when a used
textbook is purchased. There will be a training session in the use of the
software for faculty prior to the start of the
semester. The students will be expected to complete homework assignments and
quizzes on the computer throughout
the semester. The homework, quizzes, and tests will be organized and managed
through the department so as to be
consistent throughout all sections of the course.
Chapter P, Sections 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6 and 8.5: Although the material in
Chapter P should have been
mastered in a previous course, the following topics should be covered: (5
class hours)
• simplifying expressions with integral and variable exponents
• evaluating, combining and simplifying expressions involving rational exponents
and radicals
• writing rational exponents as radicals
• finding the sum, difference, product or quotient of two polynomials
• using binomial expansion for (a ±b)n
• simplifying an expression by rationalizing the denominator
• factoring by using techniques such as finding the greatest common factor of a
polynomial, factor
quadratic trinomials by into binomials, factor special products, using either
synthetic or long
division to find factors of some cubic polynomials
• finding the domain of a rational expression, reducing a rational expression to
lowest terms,
performing basic operations with rational expressions, and simplifying complex
fractions
| SECTION | TOPIC | Class hours |
| P.2 & P.3 | Integral exponents & scientific notation Rational exponents & radicals |
1 |
| P.4 & 8.5 | Operations involving polynomials including binomial expansion for (a ±b)n. |
1 |
| P.5 | Factoring polynomials | 1 |
| P.6 | Rational expressions | 2 |
Chapter 1, Sections 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, & 7: The
following topics should be covered: (8 class hours)
• solving equations in one variable, including linear, rational, and absolute
value equations
• solving a formula for a specified variable
• constructing models to solve problems involving percents, perimeter, area,
uniform motion,
mixture, and work
• finding the distance between two distinct points
• finding the midpoint of a segment connecting two points
• finding the equation of a circle satisfying given conditions
• recognizing the equation of a circle and finding its center and radius
• graphing an equation in two variables
• recognizing x- and y-intercepts
• using a graph to solve an equation
• recognizing horizontal and vertical lines by equation
• finding the slope of a line from it’s graph or by using two distinct points on
a line
• writing an equation of a line given (i) a point and a slope, (ii) two points,
(iii) a point and a line
parallel to the required line, (iv) a point and a line perpendicular to a
required line
• solving quadratic equations by factoring, completing the square, and the
quadratic formula
• using the discriminant to determine the number of real solutions
• solving a linear inequality in one variable and graph it’s solution as well as
be able to write the
solution in both set notation and interval notation
• solving absolute value inequalities
| SECTION | TOPIC | Class hours |
| 1.1 | Equations in one variable | 2 |
| 1.2 | Constructing models to solve problems | 1 |
| 1.3 | Equations and graphs in two variables | 1.5 |
| 1.4 | Linear equations in two variables | 1.5 |
| 1.6 | Quadratic equations | 1 |
| 1.7 | Linear and absolute value inequalities | 1 |
Chapter 2, Sections 1, 2, 4 and 5: The following
topics should be covered: (6 class hours)
• identifying a function
• understanding the Vertical Line Test and being able to apply it
• determining the implicit domain and range of a function defined by an
algebraic expression
• evaluating a function
• understanding and being able to interpret function notation
• determining the intercepts, domain and range of a function defined by a graph
• evaluating a function by using its graph
• graphing functions defined by linear, square root, cube root and piece-wise
expressions
• finding the sum, difference, product, quotient and composition of two
functions and state the
domain of the resulting functions
• knowing what is meant by a one-to-one function and being able to apply the
Horizontal Line Test
• finding the inverse of a function both graphically and analytically
• using composition to verify that two functions are inverses
| SECTION | TOPIC | Class hours |
| 2.1 | Functions | 1 |
| 2.2 | Graphs of relations and functions | 1 |
| 2.3 | Families of functions, transformations, & symmetry | 1.5 |
| 2.4 | Operations with functions | 1.5 |
| 2.5 | Inverse functions | 1 |
Chapter 3, Sections 1 & 5: The following topics
should be covered: (4 class hours)
•writing a quadratic function in the forms 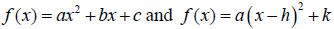
• finding the vertex and axis of symmetry of a parabola defined by a quadratic
function and sketch
its graph
• determining the extreme value of a quadratic function and know the
significance of the sign of the
coefficient of the square term
• solving equations by factoring
• solving radical equations and check for extraneous solutions
• solving equations that can be written in quadratic form
• solving absolute value equations
| SECTION | TOPIC | Class hours |
| 3.1 | Quadratic functions and inequalities | 2 |
| 3.5 | Miscellaneous equations | 2 |
Chapter 4, Sections 1,2 and 3: The following topics
should be covered: (5 class hours)
• definitions of exponential and logarithmic functions and their properties
(domain, range, intercept,
asymptote)
• sketching the graph of exponential and logarithmic functions without using a
calculator
• the number e
• analytical and graphical relationships between exponential and logarithmic
functions
• know the Laws of Logarithms and use them to simplify logarithmic expressions
• solving logarithmic equations and checking for extraneous solutions
• solving exponential equations
• solving problems involving exponential and logarithmic functions
| SECTION | TOPIC | Class hours |
| 4.1 | Exponential functions and their applications | 1 |
| 4.2 | Logarithmic functions and their applications | 1 |
| 4.3 | Rules of logarithms | 1 |
| 4.4 | More equations and applications | 2 |
Chapter 5, Sections 1 and 3: The following topics
should be covered: (2 class hours)
• solving systems of linear or non-linear equations in two variables by
elimination and/or
substitution
• determining when a system has no solution or infinitely many solutions
| SECTION | TOPIC | Class hours |
| 5.1 | Systems of linear equations in two variables | 1 |
| 5.3 | Nonlinear systems of equations | 1 |
Total 30 class lecture hours.


