MMPT OBJECTIVES
The MMPT
The MMPT is a test used at MU to:
• place students who score 19 or above into College Algebra,
Math 1100 or 1120
• place students who score 21 or above into Pre-Calculus,
Math 1160
• place students who score 26 or above into Finite Math,
Math 1300
• place students who score 26 or above into Calculus,
namely: Math 1320, Math 1400, or Math
1500.
• exempt students who score 26 or above from taking College
Algebra (Math 1100 or Math
1120).
• offer any student who scores 26 or above 3 credit hours towards
their College Algebra general
education requirement.
The MMPT is a 60-minute timed test, which consists of 40 multiple-choice
questions, all
equally weighted. The maximum possible score is 40.
MMPT OBJECTIVES
Hierarchy of Operations
Be able to:
• apply the proper order of operations when evaluating an arithmetic
expression
• apply the proper order of operations when working with algebraic
expressions.
Factoring
Be able to factor polynomials over the integers:
1. By factoring the GCF
2. By regrouping of the terms
3. By applying the basic identities:
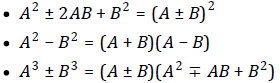
Rational Expressions
Be able to:
• Simplify, multiply, divide, add and subtract rational expressions
• Simplify complex fractions.
Exponents and Radicals
Be able to:
• apply the laws of exponents to simplify, multiply and divide expressions
involving integer and/or
rational exponents
• evaluate numbers raised to rational exponents and resulting in a
rational number
• write in radical form expressions containing rational exponents and
simplify the answer.
• write in exponent form a radical expression and simplify the answer.
• apply the laws of radicals to simplify, add, subtract, multiply and
divide radical expressions
• rationalize numerators or denominators.
Equations
Be able to solve:
• linear equations
• quadratic equations by factoring
• quadratic equations over the complex numbers using the quadratic formula
• polynomial equations over the complex numbers by factoring
• rational equations
• absolute value equations
• equations in quadratic form
• equations that involve radicals
• exponential equations
• logarithmic equations
• literal equations
• systems of equations in two variables
• trigonometric equations
Inequalities
Be able to solve:
• linear inequalities in one variable
• compound inequalities
• absolute value inequalities
• quadratic inequalities
• easily factorable polynomial inequalities
• rational inequalities
Functions
Be able to:
• tell whether a given relation is also a function
• given a function f (x) , evaluate f (a) for some given value a
• given a function f (x) , simplify the expression:
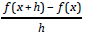
• find the domain and the range of a given relation or function
• tell whether a function is even, odd or neither
• perform operations with functions (addition, subtraction,
multiplication, division & composition
of functions) stating the domain of definition of the resulting function
• find the inverse of a given function
• Apply rigid & /or non-rigid transformations on the basic functions
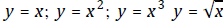 ;
;
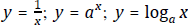 to graph related functions, or given the
graph of functions obtained
to graph related functions, or given the
graph of functions obtained
through transformations of those basic functions, determine their equation.
Midpoint, Distance & Equations of Circles
Given the coordinates of two points A & B , be able to:
• determine the coordinates of the midpoint M of the segment
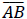
• determine the distance from A to B
Be able to:
• find an equation of the circle given its center and radius
• given the equation of a circle determine its center and radius
• solve problems related to midpoint, distance and equations of circles.
Linear Functions
Be able to:
• find the slope of the line through two given points
• find the equation of a line given some of its properties or
characteristics
• determine whether two lines are parallel, perpendicular, or neither
• find the equation of a line parallel or perpendicular to a given line
• find the coordinates of the point of intersection of two given lines
• find the equation and the slope (if any) of vertical or horizontal lines
• determine the x - & y - intercepts of a line, given it equation.
Quadratic Functions
Be able to:
• determine the coordinates of the x - & y - intercepts of a quadratic
function.
• express a quadratic function f = xax2 + bx + c in the form: f
(x) = a(x − h)2 + k
• determine the concavity of a quadratic function
• determine the coordinates of the vertex (the max or min) of a quadratic
function
• determine the maximum or minimum value of a quadratic function
• determine the domain and the range of a quadratic function
• apply ones knowledge of the role that the sign of ‘a’, 'b2 −
4ac', and ‘c’ play in the graph of the
parabola y = ax2 + bx + c, to match the graph of parabolas with such
characteristics.
• match the graph of quadratic functions with their equation.
Piecewise-Defined Functions
Be able to:
• graph a given piecewise defined function.
• match the graph of a piecewise-defined function with its equation.
Polynomial Functions
Be able to:
• determine the end-behavior of a given polynomial function
• find the y-intercept and the x -intercepts of polynomial functions that
factor easily over the
integers
• find the multiplicity of the real zeros of a polynomial function
• match the graph of polynomial functions with their equations
• apply the factor theorems and the remainder theorem in problem solving.
Rational Functions
Be able to:
• do a long division of a polynomial by a polynomial
• determine the horizontal and vertical asymptotes of rational functions
• determine the y - & x - intercepts of rational functions, if any
• match the graph of rational functions with their equation.
Exponential Functions
Be able to:
• determine the equation of the horizontal asymptote of such functions
• determine the y - & x -intercept(s) of such functions
• match the graph of such functions with their equation.
Logarithmic Functions & Properties of Logarithms
Be able to:
• express a logarithmic form into exponential form and an exponential form
into logarithmic form.
• match the graph of logarithmic functions of the form:
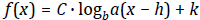 with their
with their
equation.
• determine the equation of the vertical asymptote of such functions
• determine the x - & y -intercepts of such functions
• match the graph of such functions with their equations.
• apply the properties of logarithms to evaluate or simplify logarithmic
expressions
Translate from Degrees into Radians (or π-radians)
and from Radians into Degrees
Trig Ratios of the Special Angles (0°, 30°, 60°, 90°)
Be able to:
• determine the trig ratio of angles that can be deduced from those of the
special angles (0°, 30°,
60°, 90°).
• determine the inverse trig value of certain numbers such as:
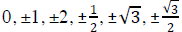 , etc.
, etc.
Trig Ratios of Angles
Be able to:
• determine all the other five trig ratios of an angle, given the value of
one of its trig ratios and the
quadrant in which the terminal side of the angle lies.
• Given one of the trig ratios of an angle x determine the trig ratios of
the angles: – x, (π, − x) or
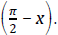
• Use the sum, difference, half-angle and double-angle formulas to
determine the trig ratios of other
angles.
Solve triangles
Be able to:
• solve a right triangle given some of the sides or angles.
• apply the law of sines and the law of cosines to solve oblique
triangles.
Graphing Trig Functions & their Inverses
Be able to:
Match trig functions or inverse trig functions of the form given below with
their graph.
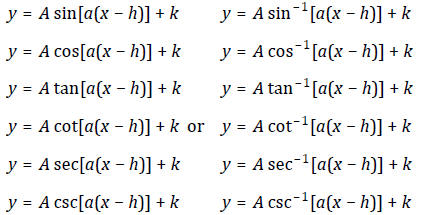
Search
This page was last updated Thursday, February 5, 2009


